Imagine this: your agency just landed a fantastic new e-commerce client. The celebration is short-lived, though. During the kickoff call, they casually mention their product catalog has 15,000 SKUs.
Suddenly, that exciting win feels like an operational nightmare.
How do you possibly write unique, SEO-optimized descriptions for thousands of products without spending a year on it? The old method—handing the task to a junior copywriter with a massive spreadsheet—is a direct path to burnout, budget overruns, and inconsistent results. It’s the scaling problem that has plagued e-commerce SEO for years. The bottleneck isn’t talent; it’s time.
For agencies, this challenge represents both a threat and a massive opportunity. The threat is getting bogged down in manual, low-margin tasks. The opportunity is to build a scalable, AI-powered system that turns this impossible task into a profitable service.
The Vicious Cycle of E-commerce Content at Scale
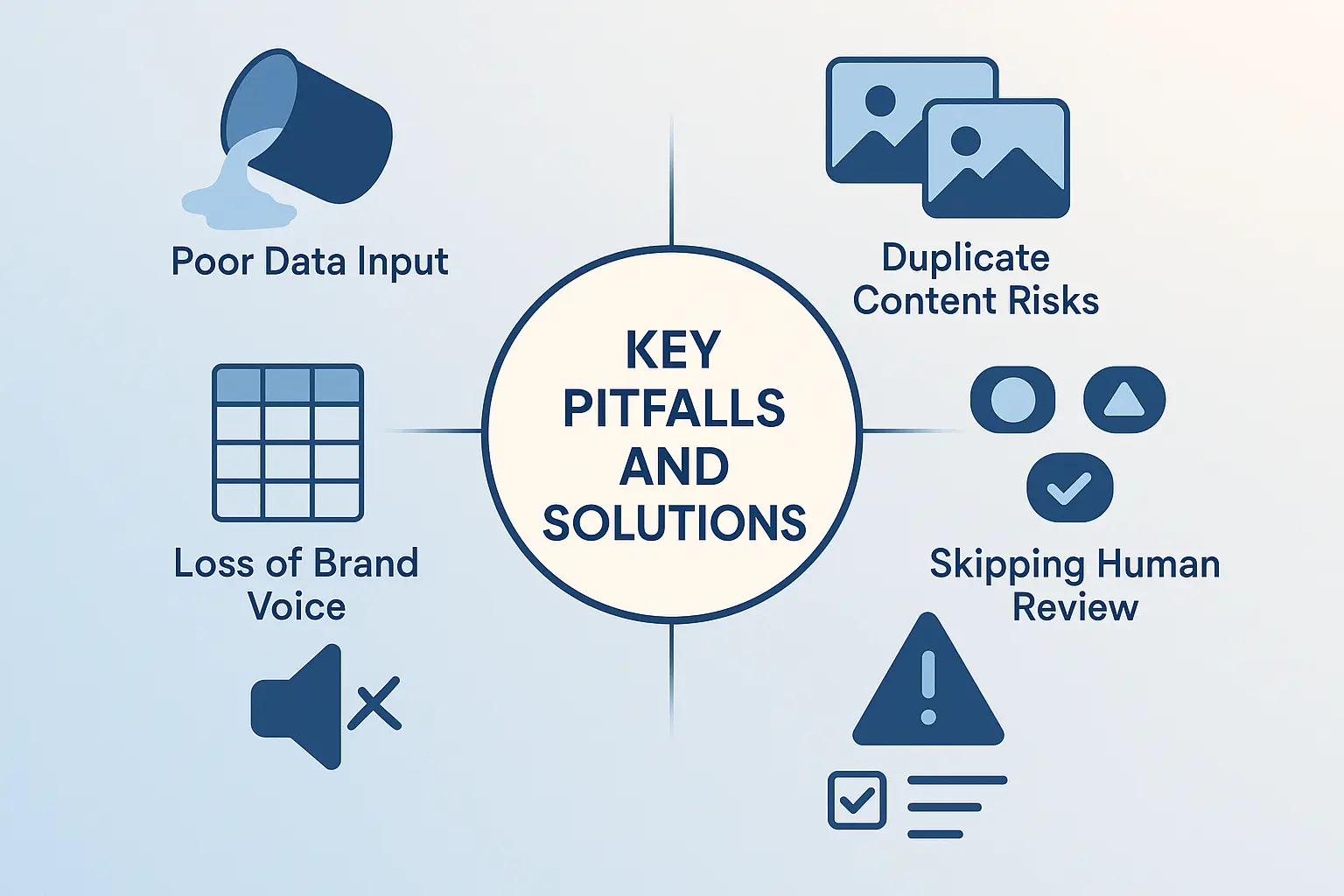
Most large e-commerce sites suffer from the same set of content issues, creating a vicious cycle that suppresses organic growth:
- Manufacturer Descriptions: The most common shortcut is to copy and paste descriptions provided by the manufacturer. The problem? Every other retailer is doing the same thing, leading to massive duplicate content issues across the web.
- Thin Content: To avoid duplication, some sites default to a few generic sentences. This creates “thin content” pages that Google sees as low-value, offering little to no unique information for the user.
- Missed Keyword Opportunities: Without a proper optimization process, thousands of product pages miss out on targeting valuable long-tail keywords (e.g., “women’s waterproof merino wool hiking socks”) that high-intent buyers use.
Manually fixing this for a 15,000-product catalog is, frankly, impossible for most agencies. If a skilled copywriter takes just 20 minutes per product, you’re looking at 5,000 hours of work. That’s more than two years of full-time effort for a single person.
This is where artificial intelligence changes the equation. It’s not about replacing strategists; it’s about empowering them with a tool that can execute their strategy at an unprecedented scale.
Why AI Is the Engine for E-commerce SEO
The apprehension around using AI for content is understandable, but the conversation has shifted. It’s no longer a fringe experiment; it’s a core business tool. Research shows that 97% of business owners believe AI will be a positive force for their company, and for good reason. For agencies, the primary benefit is a dramatic increase in efficiency.
When 64% of businesses expect AI to increase productivity, they’re thinking of workflows exactly like this one. AI collapses the time it takes to get from a blank page to a high-quality, optimized draft, freeing up your team to focus on strategy, analysis, and client relationships. This isn’t automation for the sake of automation; it’s about making your experts’ jobs easier and more impactful.
Let’s build the workflow that makes this happen.
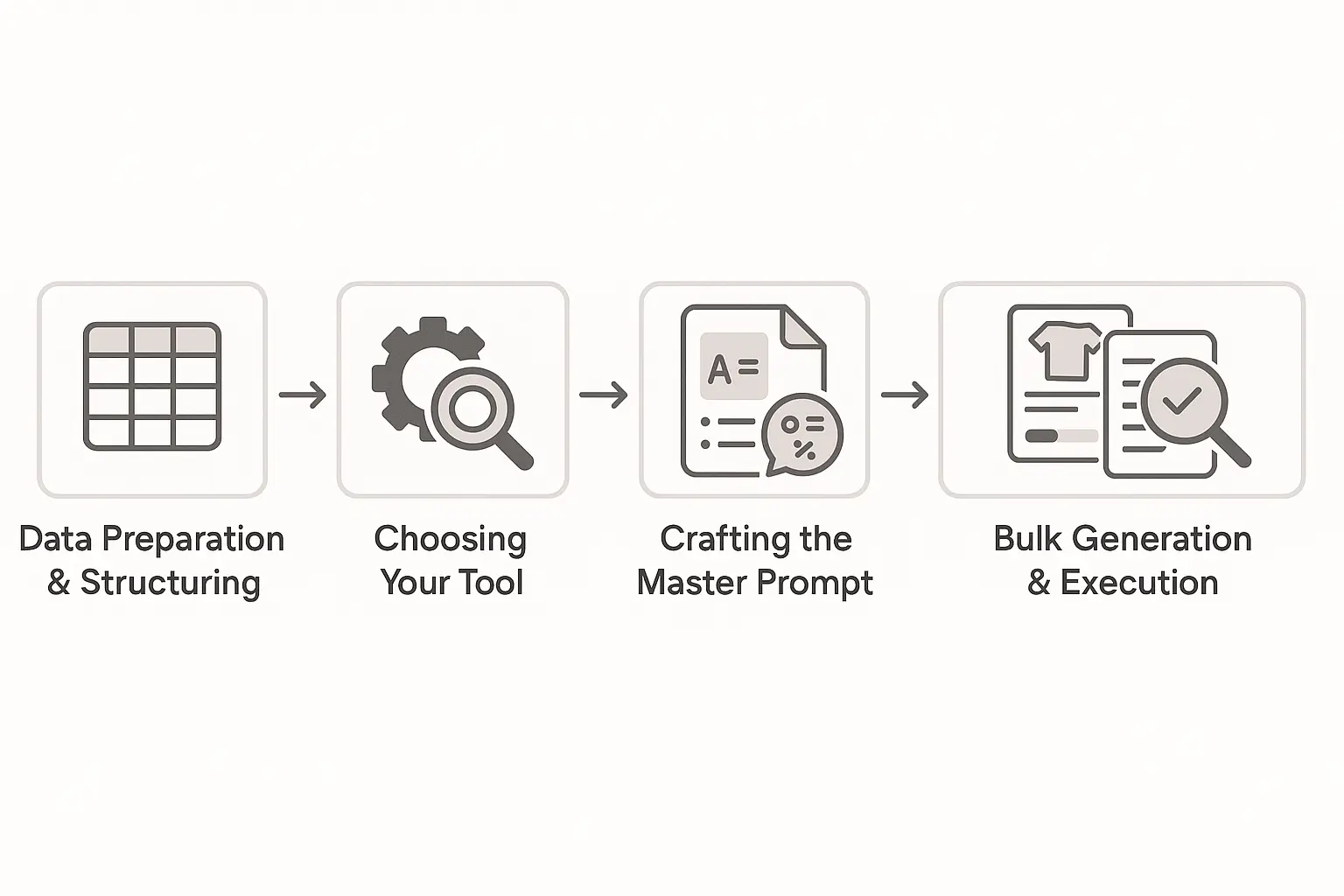
The 4-Step AI Workflow for Optimizing Product Descriptions
This isn’t about asking an AI to “write a product description.” That approach leads to generic, uninspired copy. An effective, scalable system is built on a foundation of good data and smart instructions.
Step 1: Gather Your Foundational Data
Great output requires great input. Before you write a single prompt, you need to collect and structure your data. For each product, you’ll want a clear, spreadsheet-ready list of its core attributes:
- Product Name: The official name of the item.
- Category/Type: e.g., Running Shoe, V-Neck Sweater, etc.
- Key Features: What makes it special? (e.g., GORE-TEX fabric, 100% organic cotton, noise-canceling technology).
- Core Specs: Material, dimensions, weight, color options, etc.
- Target Audience: Who is this for? (e.g., marathon runners, casual hikers, busy parents).
- Brand Voice: A few keywords describing the tone (e.g., professional, witty, adventurous, minimalist).
A comprehensive white-label SEO audit is invaluable here, helping you prioritize which product categories or pages have the biggest SEO gaps and should be tackled first.
Step 2: Map Keywords at Scale
You can’t manually research keywords for 10,000 products. Instead, you map them programmatically.
Start by identifying keyword patterns for each product category. For “running shoes,” for instance, the patterns might include:
- [gender]’s [type] running shoes: “men’s trail running shoes”
- best running shoes for [condition]: “best running shoes for flat feet”
- [brand] [model name] review: “Brooks Ghost 15 review”
You can then use a formula in your spreadsheet to combine these patterns with your product attributes, generating a primary and secondary keyword for each SKU. This systematic approach lets you deliver effective white-label keyword research without the manual time sink.
Step 3: Engineer the “Master Prompt”
This is where the magic happens. A master prompt is a template you can apply to every product in your catalog. It uses variables from your spreadsheet to give the AI tailored instructions for each one.
Here’s a simplified example of a master prompt structure:
Role: You are an expert e-commerce copywriter specializing in SEO.
Task: Write a compelling, 150-word product description for the following item.
Tone of Voice: Adopt a [{Brand Voice}] tone.
Product Name: [{Product Name}]
Product Details:
- Category: [{Category}]
- Key Features: [{Key Features}]
- Specifications: [{Core Specs}]
- Target Audience: This product is for [{Target Audience}].
SEO Instructions:
- Naturally include the primary keyword: “[{Primary Keyword}]” in the first 50 words.
- Naturally include the secondary keyword: “[{Secondary Keyword}]” somewhere in the description.
- Focus on the benefits of the features, not just listing them. Explain how they help the [{Target Audience}].
- End with a clear call-to-action.
- Do not use clichés like “game-changer” or “unleash the power.”
You can see how plugging data from your spreadsheet into this template creates a unique, highly specific set of instructions for the AI to follow.
Step 4: Bulk Generation and Human Review
With your data and master prompt ready, you can use AI tools or APIs (like those from OpenAI or Anthropic) connected to your spreadsheet to generate descriptions for all 15,000 products in a matter of hours, not years.
This is the most critical part: The AI generates the first draft. A human editor provides the final polish.
 From Manual Grind to Strategic Growth
From Manual Grind to Strategic Growth
This workflow does more than just solve the product description problem; it changes what your agency is capable of. Once this system is in place, you can handle clients of any size. That 100,000-SKU prospect that used to be terrifying is now your ideal client.
You’re no longer selling hours of tedious copywriting. You’re selling a scalable, efficient SEO solution that drives real results. By embracing AI-powered SEO services for agencies, you shift your team’s focus from mundane execution to high-value strategy and position your agency as a forward-thinking partner.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will Google penalize me for using AI-generated content?
No. Google’s official guidance is clear: they reward high-quality, helpful content, regardless of how it was produced. Their systems are designed to detect spammy, low-value content, not the method of generation. As long as your final, human-reviewed descriptions are accurate, unique, and helpful to the user, you’re operating well within Google’s guidelines.
How do I maintain a consistent brand voice with AI?
Consistency comes from your master prompt. By including detailed instructions on tone, style, words to use, and words to avoid, you guide the AI toward copy that aligns with the brand. The final human review step is the ultimate check to ensure every piece of copy is perfectly on-brand.
What kind of tools do I need for this process?
You don’t need a single, all-in-one tool. This workflow can be built using a combination of common business tools:
- Spreadsheet Software: Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel for data organization.
- A Large Language Model (LLM): Access to an AI model like GPT-4 via its API or a third-party tool that integrates with spreadsheets.
- SEO Tools: For the initial keyword research and pattern identification.
Isn’t this just creating another form of duplicate content?
Quite the opposite. A well-engineered prompt uses the unique attributes of each product (color, size, material, features) as inputs. This forces the AI to generate a distinct description for each SKU, solving the very duplicate content problem that arises from using a single manufacturer description everywhere. The goal is uniqueness at scale.