Imagine this: your client lands a major feature in an industry-leading publication. The article mentions their brand by name, praises their innovation, and positions them as an expert. It’s a massive win for their brand visibility.
There’s just one problem: there’s no link back to their website.
In the past, an SEO might have sighed and written it off as a missed opportunity for ‘link juice.’ Today, however, the game has changed. That unlinked mention is an incredibly valuable signal—if search engines can understand who it’s about.
In the age of AI-powered search, ensuring Google and other engines can correctly connect these dots isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s fundamental to building lasting brand authority. This is the core of Entity SEO.
From Keywords to Concepts: The Big Shift to Entity SEO
For years, SEO was about keywords—the literal ‘strings’ of text people typed into a search bar. But search engines have evolved. They no longer just match strings; they understand ‘things.’
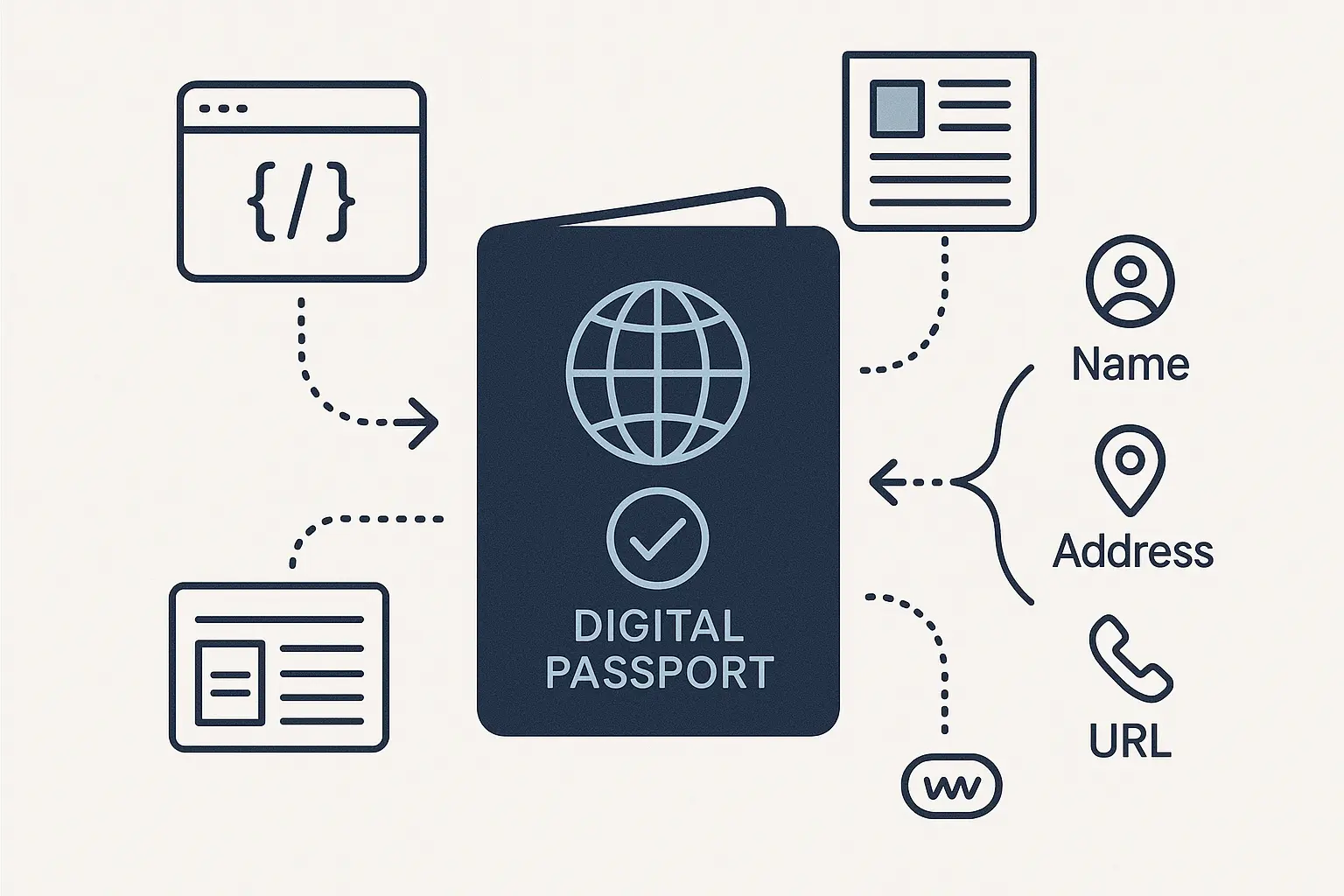
An entity is any well-defined thing or concept that is unique, distinguishable, and verifiable. It can be a person (Elon Musk), a place (the Eiffel Tower), a brand (Coca-Cola), or a concept (digital marketing).
Google’s Knowledge Graph is its massive encyclopedia of these entities and the relationships between them. It doesn’t just see the letters ‘A-p-p-l-e’; it understands the difference between Apple the tech company, apple the fruit, and Apple Records.
This shift from ‘strings to things’ is why Entity SEO is so critical. It’s the practice of defining your client’s brand as a clear, unambiguous entity and communicating that identity to search engines, allowing them to connect every mention, review, and article back to the source—with or without a link.
Why AI Search Makes Entity SEO Non-Negotiable
The rise of AI-driven search experiences, like Google’s AI Overviews, has made this more urgent than ever. AI models need to be extremely confident in the information they use to generate answers. They rely on the Knowledge Graph’s web of verified facts to build that confidence.
If your client’s brand entity is weak, ambiguous, or has conflicting information scattered across the web, an AI model won’t trust it. It will favor a competitor with a stronger, clearer digital identity when crafting its answers.
The stakes are high. According to a study by Milestone Research, 74% of enterprise marketers report that entity search is a high or essential priority. They understand that to be visible in AI-driven search, you don’t just need to rank—you need to be recognized as an authoritative entity.
The Hidden Threat: When AI Can’t Connect the Dots
What happens when a search engine can’t confidently attribute a brand mention? It gets lost in the noise. The mention exists, but it doesn’t contribute to your client’s authority. This ambiguity is the enemy of modern SEO.
This confusion often stems from common issues:
- Name Ambiguity: Your client’s brand name is similar to another company’s, or it’s a common word (e.g., ‘Thrive’ for a marketing agency).
- Inconsistent Data: Old addresses, outdated phone numbers, or slight variations in the company name across different online directories and social profiles.
- Unlinked Mentions: Positive press or reviews that mention the brand by name but fail to link back, leaving it up to Google to make the connection.
When AI encounters this messy digital footprint, it can’t be sure which ‘Thrive’ the article is talking about. As a result, that valuable signal of authority is lost.
The Core Components of a Strong Brand Entity
So, how do you fix this? By building a clear, consistent, and interconnected digital identity for your client. Your two most powerful tools for the job are structured data and consistent NAPU.
1. The Power of Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Think of Schema markup as a translator that speaks directly to search engines. It’s code you add to your client’s website that explicitly tells them what everything is. Instead of letting Google guess that your client is a local marketing agency in Austin, you can use LocalBusiness schema to tell it directly.
Key schema types for building an entity include:
- Organization or LocalBusiness: This is the foundation. It defines the business name, address, logo, and official website.
- sameAs: This property is a superpower for entity building. Within your Organization schema, you can use sameAs to link to your client’s official social media profiles, Wikipedia page, Crunchbase profile, and other authoritative sources. This weaves a web of verified connections, essentially telling Google, ‘All of these profiles belong to the same entity.’
- Person: Establishes key individuals (like the CEO or founder) as entities in their own right, linked to the main organization.
By implementing comprehensive schema, you’re removing all guesswork for search engines.
2. The Unsung Hero: Consistent NAPU
NAPU stands for Name, Address, Phone, and URL. While it sounds basic, consistency across the web is a cornerstone of a strong entity, especially for local businesses.
Every time Google finds your client’s business mentioned online with the exact same NAPU, it acts as another vote of confidence, reinforcing its understanding of the entity.
Conversely, inconsistencies create confusion. An old address on a forgotten directory listing or a different phone number on a social profile can weaken the entity and erode trust—not just with search engines, but with customers. A BrightLocal survey found that 80% of consumers lose trust in local businesses if they see incorrect or inconsistent contact details or business names online.
Your Action Plan: How to Solidify Your Client’s Digital Identity
Building a strong brand entity is a foundational strategy that pays long-term dividends. Here’s a straightforward action plan to get started:
- Establish a ‘Source of Truth’: Your client’s website is the canonical source. Ensure its Organization or LocalBusiness schema is perfectly implemented and all information is accurate.
- Conduct a NAPU Audit: Systematically check and correct listings across major directories like Google Business Profile, Yelp, and industry-specific sites. For a deeper dive into finding these issues, our guide on white-label technical SEO audits can help you spot inconsistencies at scale.
- Connect Profiles with sameAs: Audit your client’s Organization schema to ensure you’re using the sameAs property to link to all relevant, high-authority profiles.
- Monitor and Standardize Brand Mentions: When your client gets new press, encourage journalists to use the official brand name. While you can’t always get a link, ensuring the name is correct helps Google connect the mention back to the core entity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Entity SEO
What’s the difference between Entity SEO and traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on keywords and backlinks, while Entity SEO concentrates on building a verifiable, authoritative identity for a brand. This allows search engines to understand the concept behind the keywords and attribute all mentions (linked or unlinked) to that brand.
How do I know if my client has a Knowledge Panel?
A Knowledge Panel is a strong signal that Google recognizes your client as an entity. To check, just Google their exact brand name. If a box with their logo, description, and business details appears on the right side of the search results, they have one.
Does every unlinked mention help my SEO?
An unlinked mention only helps if Google can confidently connect it to the right entity. If your client’s digital identity is ambiguous, the mention may have little to no impact.
Can I build an entity for a person, not just a company?
Absolutely. Using Person schema, you can establish founders, executives, or key team members as their own entities, linking them to the main Organization. This is crucial for building thought leadership.
How long does it take to see results from Entity SEO?
Entity SEO is a long-term, foundational strategy. It’s not about quick wins; it’s about building an unshakeable authority that will pay dividends for years, especially as AI continues to shape the search landscape. This foundation is a core part of our white-label SEO services.
From Mentions to Authority: The Future is Connected
In an AI-driven search world, being understood is more powerful than simply being seen. Entity SEO is the work of ensuring your client’s brand is unambiguously understood by the algorithms that now dictate online visibility.
By meticulously crafting a consistent and interconnected digital identity through structured data and clean NAPU, you transform scattered brand mentions into a powerful chorus of authority. You’re not just chasing keywords; you’re building a brand that AI trusts and promotes.
Ready to help your clients build unshakeable brand authority that’s ready for the future of search? Learn how our approach to SEO outsourcing for agencies can provide the scalable execution you need to make it happen.

